Transform your social media into an effective marketing tool. In our comprehensive guide to social marketing, you’ll find insider information, effective suggestions, and tried-and-true tactics.
Introduction
Social marketing is an essential strategy for businesses aiming to connect with their audience, build brand awareness, and drive meaningful engagement. With the rise of social media platforms and digital communities, leveraging these tools effectively can set your business apart from competitors.
This guide will walk you through the fundamentals, strategies, and advanced techniques necessary to master social marketing. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced marketer, this comprehensive guide has something for everyone.
What is Social Marketing?
At its core, social marketing is using commercial marketing principles to influence behaviours that benefit society. Unlike traditional marketing, which attempts to sell items or services, social marketing focuses on creating change for the better.. For example, campaigns encouraging seatbelts, reducing plastic usage, or promoting vaccination programs illustrate the concept in action.
Social marketing is often confused with societal marketing. While they share similarities, societal marketing emphasises the balance between consumer needs, societal welfare, and organisational profits. Examples of societal marketing concepts include eco-friendly packaging or fair trade products that cater to consumer preferences while benefiting the environment or underserved communities.
Why Is Social Marketing Important?
Social marketing is a powerful tool for achieving goals across business and societal domains. Its importance lies in its ability to:
Increase Brand Awareness
To increase brand awareness through social marketing, you must share interesting material that resonates with your target audience on a continuous basis. By regularly posting valuable, relevant information, your brand stays visible and top-of-mind. Social marketing allows brands to showcase their leadership in addressing societal issues, positioning them as responsible and trustworthy.
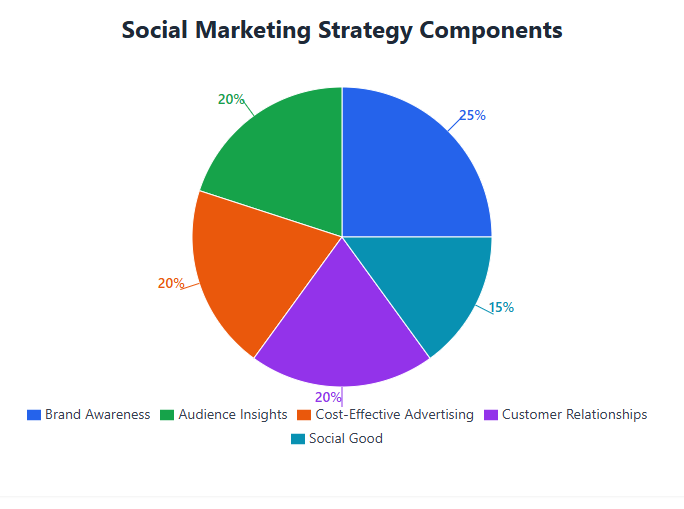
Representing the largest portion at 25%, brand awareness is clearly the cornerstone of a social marketing strategy. This significant allocation reflects the fundamental importance of consistently sharing engaging content to foster visibility and build trust.
In this digital age, tools like NFC-enabled social media cards can further amplify your efforts. These innovative cards allow users to share their social media profiles or business details with a single tap, offering a modern and efficient way to enhance your online presence. By integrating social media cards into your strategy, you make it easier for your audience to connect, follow, and engage with your brand instantly.
This proactive engagement builds positive associations with your audience. As your brand consistently aligns with social good, it cultivates deeper emotional connections. As the highest priority component, brand awareness serves as the foundation for all other marketing efforts. Ultimately, effective brand awareness strategies foster long-term loyalty and trust with your audience, making it the essential building block for a successful social marketing campaign.
Provide Audience Insights
Enable Cost-Effective Advertising
Foster Customer Relationships
Promote Social Good
Social Marketing vs. Commercial Marketing
While both share foundational principles, their goals and outcomes differ significantly:
Commercial Marketing
- Focuses on increasing sales and profits by meeting consumer demands.
- Example: Advertising a new product to boost revenue.
Social Marketing
- Seeks to promote societal welfare by influencing behaviors for social good.
- Example: Campaigns promoting road safety by encouraging the use of seatbelts.
Key Differences
- Audience: Commercial marketing targets consumers, while social marketing often addresses demographics facing societal challenges.
- Outcome: Success in commercial marketing is measured by revenue, while social marketing success is gauged by behavioral change and societal impact.
Models of Social Marketing
The Four Ps
Similar to commercial marketing, social marketing relies on the Four Ps of social marketing:
- Product: The desired behavior or solution. Example: Encouraging vaccination to prevent diseases.
- Price: The cost or barriers associated with adopting the behavior. Example: Reducing misconceptions about vaccination side effects.
- Place: The channels where the target audience can access information or resources. Example: Community centers, hospitals, and social media platforms.
- Promotion: The strategies used to communicate the message effectively. Example: Running awareness campaigns via TV, radio, and online ads.
Community-Based Social Marketing (CBSM)
This model emphasizes localized, grassroots efforts to drive change within specific communities. CBSM is particularly effective for environmental and public health initiatives, as it prioritizes direct engagement and measurable outcomes.
- Example: Encouraging recycling in local neighborhoods by providing easy access to recycling bins and hosting educational workshops.
- Additional Insight: CBSM campaigns foster a sense of ownership and participation among community members.
Social Marketing Theories
Theories like the Health Belief Model or Social Cognitive Theory offer valuable frameworks for understanding audience behavior and crafting impactful campaigns.
- Application: The Health Belief Model helps address perceived barriers and boosts self-efficacy, improving campaign effectiveness.
- Example: Anti-obesity initiatives that emphasize the personal and societal benefits of healthy living.
Advanced Techniques in Social Marketing
Influencer Collaborations
Partnering with influencers can significantly amplify your message by tapping into their established trust and audience. To maximize success, it’s crucial to choose influencers whose values align with your brand, ensuring authentic connections. Focus on building genuine relationships through collaborations rather than simply paying for endorsements. This approach fosters credibility and deeper engagement with both the influencer’s audience and your own.
Social Media Advertising
Paid social media ads are a powerful way to reach targeted audiences with precision. Retargeting ads can be used to re-engage users who have interacted with your brand before, increasing conversion rates. Additionally, leveraging lookalike audiences—groups similar to your existing customers—helps find new potential leads and expand your reach effectively.
User-Generated Content (UGC)
Encouraging followers to create and share content that features your brand is a powerful form of social proof. Hosting challenges or contests can incentivize participation and foster community engagement. Reposting user-generated content not only showcases your loyal customers but also builds a sense of belonging and involvement, enhancing brand authenticity.
Automation and Scheduling
Using tools like Canva for content creation and Later or Buffer for scheduling posts helps save time while maintaining consistency. Automation ensures your brand stays active and relevant across social platforms without requiring constant manual effort. Scheduling content in advance also allows for more strategic planning and better alignment with audience peak engagement times. This consistency improves overall campaign effectiveness and keeps your audience engaged.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Ignoring Analytics
One of the biggest mistakes in social marketing is neglecting to track and analyze performance data. Regularly reviewing analytics helps you understand what’s working and what isn’t, enabling you to adapt your strategy accordingly. Without this feedback, you may miss opportunities to optimize campaigns and improve ROI.
Overposting
While consistency is key, posting too frequently can overwhelm your audience and lead to disengagement. Overposting may appear spammy and diminish the quality of your content. Focus on creating valuable, well-timed posts that resonate with your audience, rather than prioritizing volume. Quality content will always outperform excessive posting in terms of engagement and audience retention.
Lack of Engagement
Social media is a two-way street, and failing to engage with your audience can harm your brand’s reputation. Always respond to comments, questions, and messages in a timely manner. Engaging with your community fosters trust, loyalty, and positive sentiment. Ignoring interactions can make your audience feel undervalued and diminish the relationship you’ve worked to build.
Conclusion
Social marketing is a dynamic and ever-evolving field that requires creativity, consistency, and a deep understanding of your audience. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to build a strong online presence, foster meaningful connections, and achieve your marketing goals.